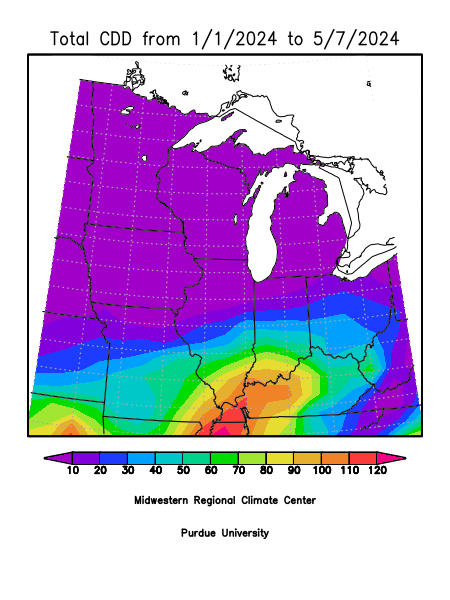
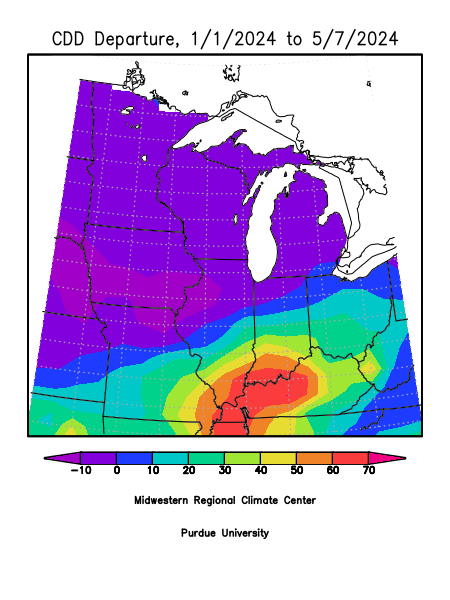
Cooling Degree Days
Cooling Degree Days (CDD) are a metric used to estimate the energy demand for cooling buildings. They measure how much (and for how long) the outside temperature is above a base temperature, typically 65°F. The higher the number of cooling degree days, the greater the need for air conditioning to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures.
For example, if the average outdoor temperature on a particular day is 75°F, that day would have 10 cooling degree days (75°F - 65°F = 10 CDD). CDDs are commonly used by utility companies, meteorologists, and building managers to assess energy consumption patterns and forecast cooling energy requirements.
CDD Departures are based on the 1991-2020 Climatological Normals.
Click maps for full image.